At Biobot, we analyze wastewater across the country for various infectious disease pathogens....

Respiratory Virus Risk Reports
Comprehensive Insights for COVID-19, Influenza, and RSV
COVID-19, Influenza, and RSV Wastewater Monitoring in the U.S. | Week of October 7, 2024
Throughout the respiratory season, we analyze wastewater for the presence of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza virus (types A and B). Together with COVID-19, these three pathogens are outsized contributors to our seasonal respiratory illness burden. In this data series, we’ll guide you through the wealth of data we’ve gathered from our Biobot Network of national sampling sites, aiming to shed light on emerging trends in respiratory virus activity and community viral load. Our goal is to equip you with information to make informed decisions.

Data Note: Samples are collected from participating locations, and processed by our lab team on a rolling basis. Each point on the figure represents the weekly average concentration, from Sunday – Saturday (corresponding to the MMWR week), aligned to that week’s Saturday.
Contributors

Marisa Donnelly, PhD
Public Health Partnerships Epidemiologist
Previous Risk Reports
Summary: Week of 10/7/24
Biobot’s national wastewater network continues to show declining concentrations of SARS-CoV-2, and very low concentrations of influenza A & B, and RSV in week 40. National hospitalization rates for COVID-19 continue to decline, currently at 1.9 per 100,000 persons in week 39. National hospitalizations rates for influenza and RSV remain very low — both have less than 0.1 hospitalizations per 100,000 persons through week 39.
The Bottom Line: While COVID-19 activity is declining and influenza and RSV are still low, now is a good time to start thinking about fall boosters before activity picks up again. Our recommendations to remain healthy are the same as they were in the winter: if you feel unwell, minimize contact with others, consider wearing a mask in crowded areas, and stay current with vaccinations and boosters.
National Outlook
COVID-19
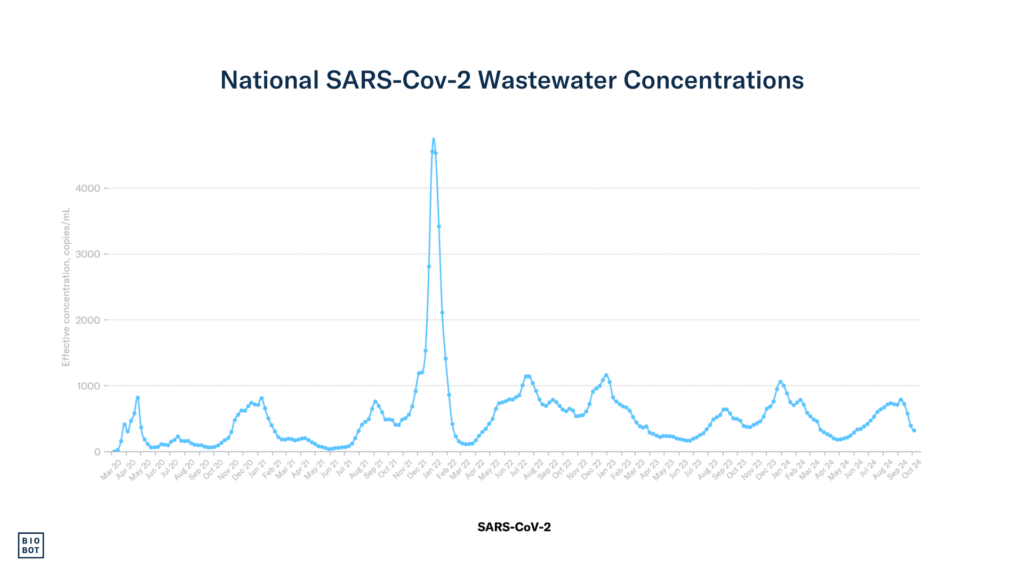
SARS-CoV-2 concentrations are continuing to decline nationally.
Influenza
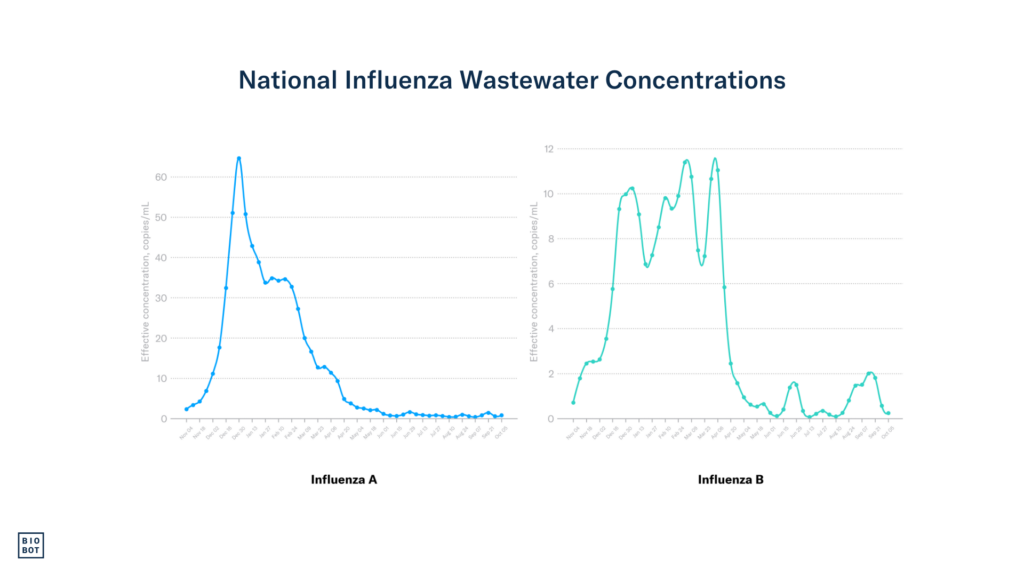
Influenza A and B concentrations remain very low nationally.
RSV
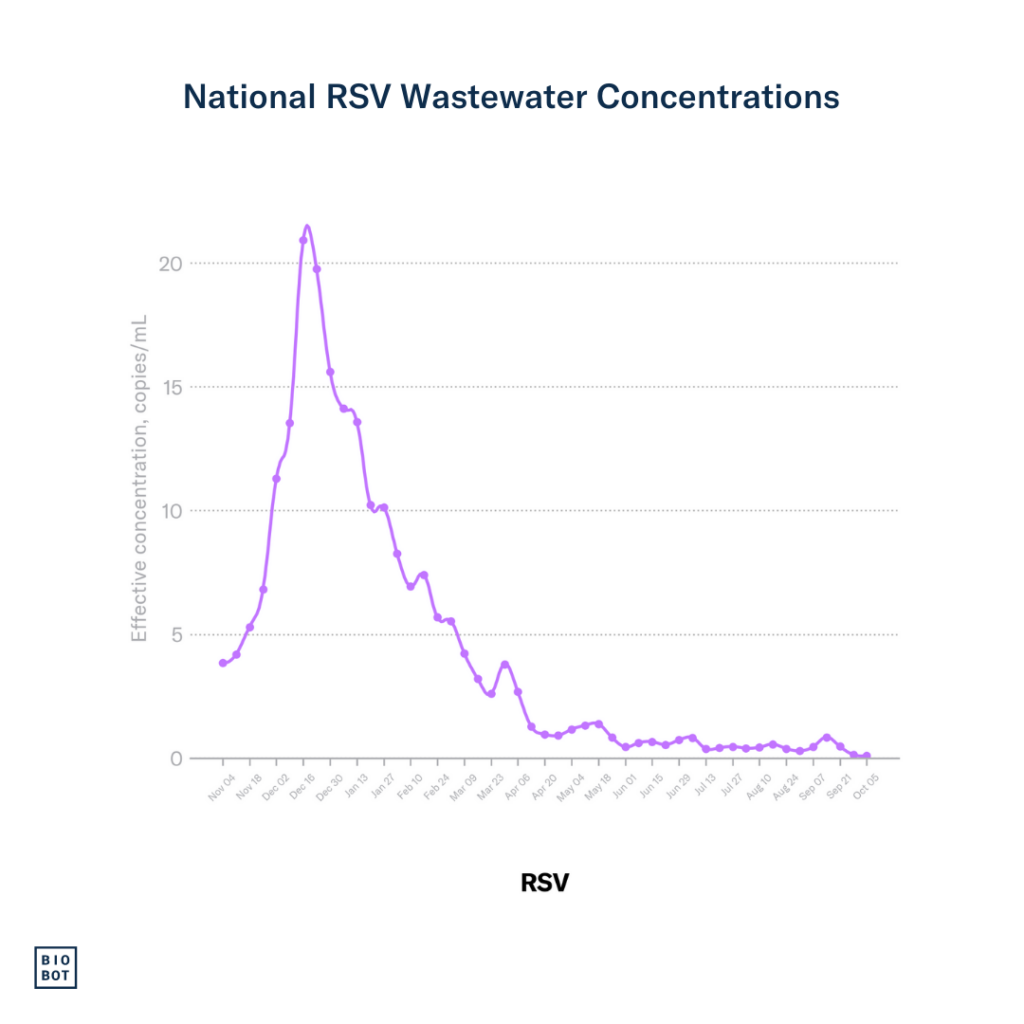
RSV concentrations remain very low nationally.
Regional
The South
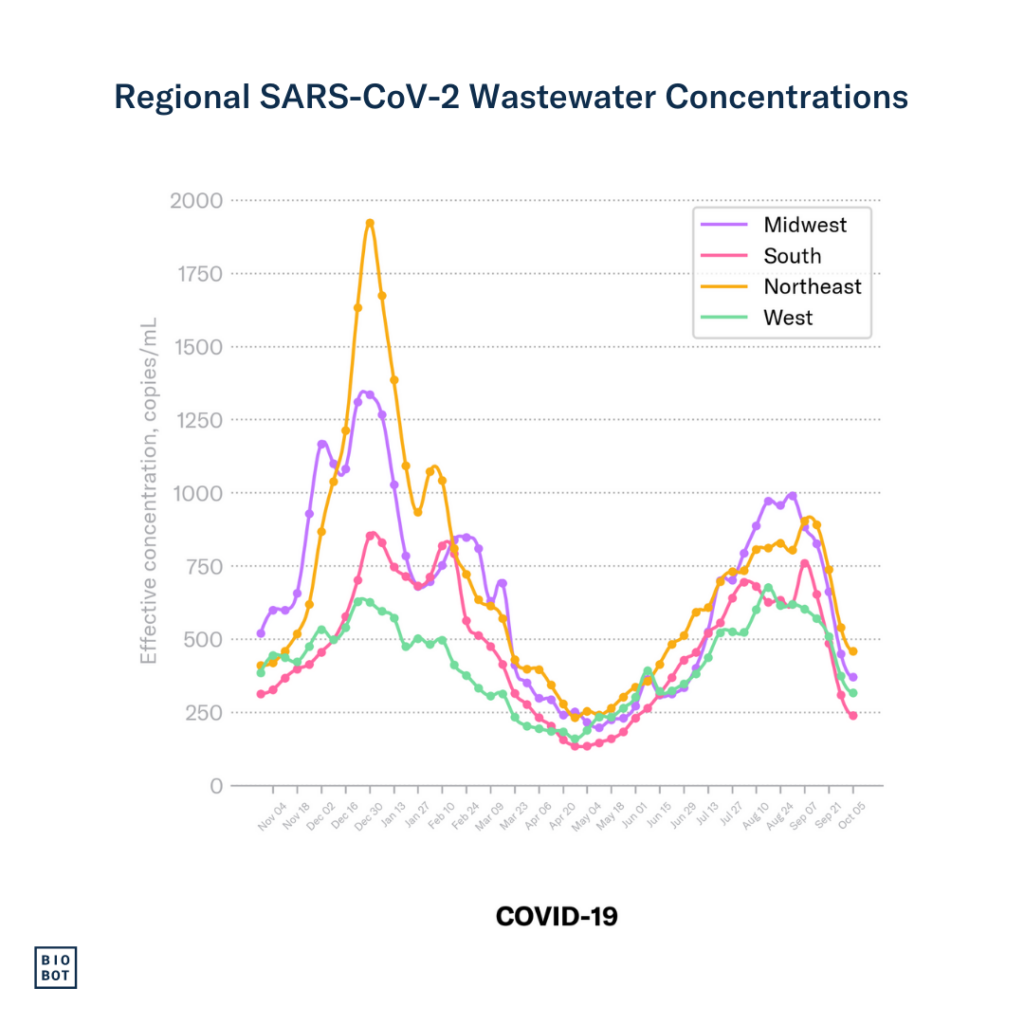
COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations in the South continue to decline.
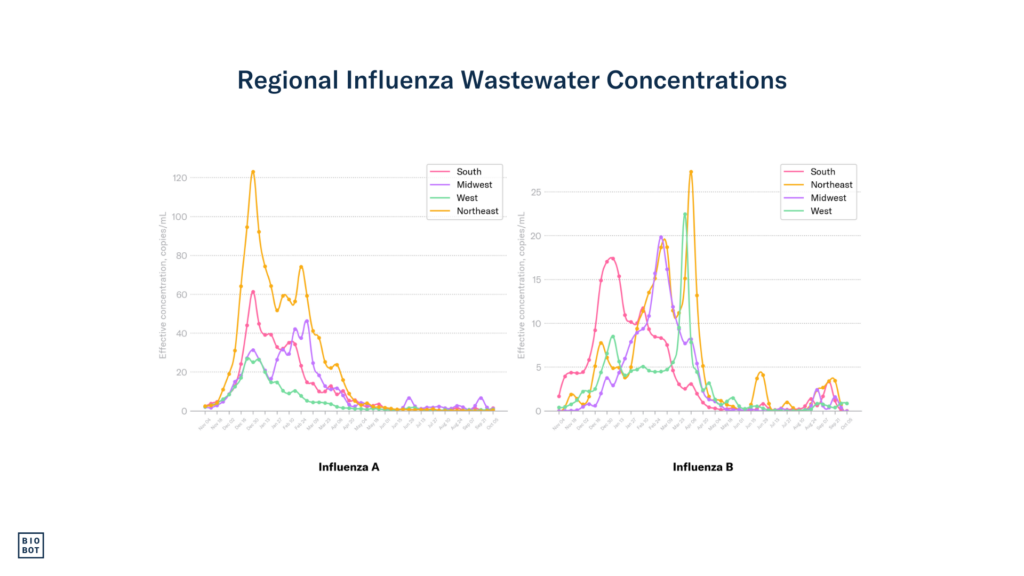
Influenza: Influenza A and B concentrations remain low in the South.
RSV: RSV wastewater concentrations remain low in the South.
The Midwest
COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations in the Midwest continue to decline.
Influenza: Influenza A and B concentrations remain low in the Midwest.
RSV: RSV wastewater concentrations remain low in the Midwest.
The Northeast
COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations in the Northeast continue to decline.
Influenza: Influenza A and B concentrations remain low in the Northeast.
RSV: RSV wastewater concentrations remain very low in the Northeast.
The West
COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations in the West continue to decline.
Influenza: Influenza A and B concentrations remain low in the West.
RSV: RSV wastewater concentrations remain very low in the West.

Footnotes:
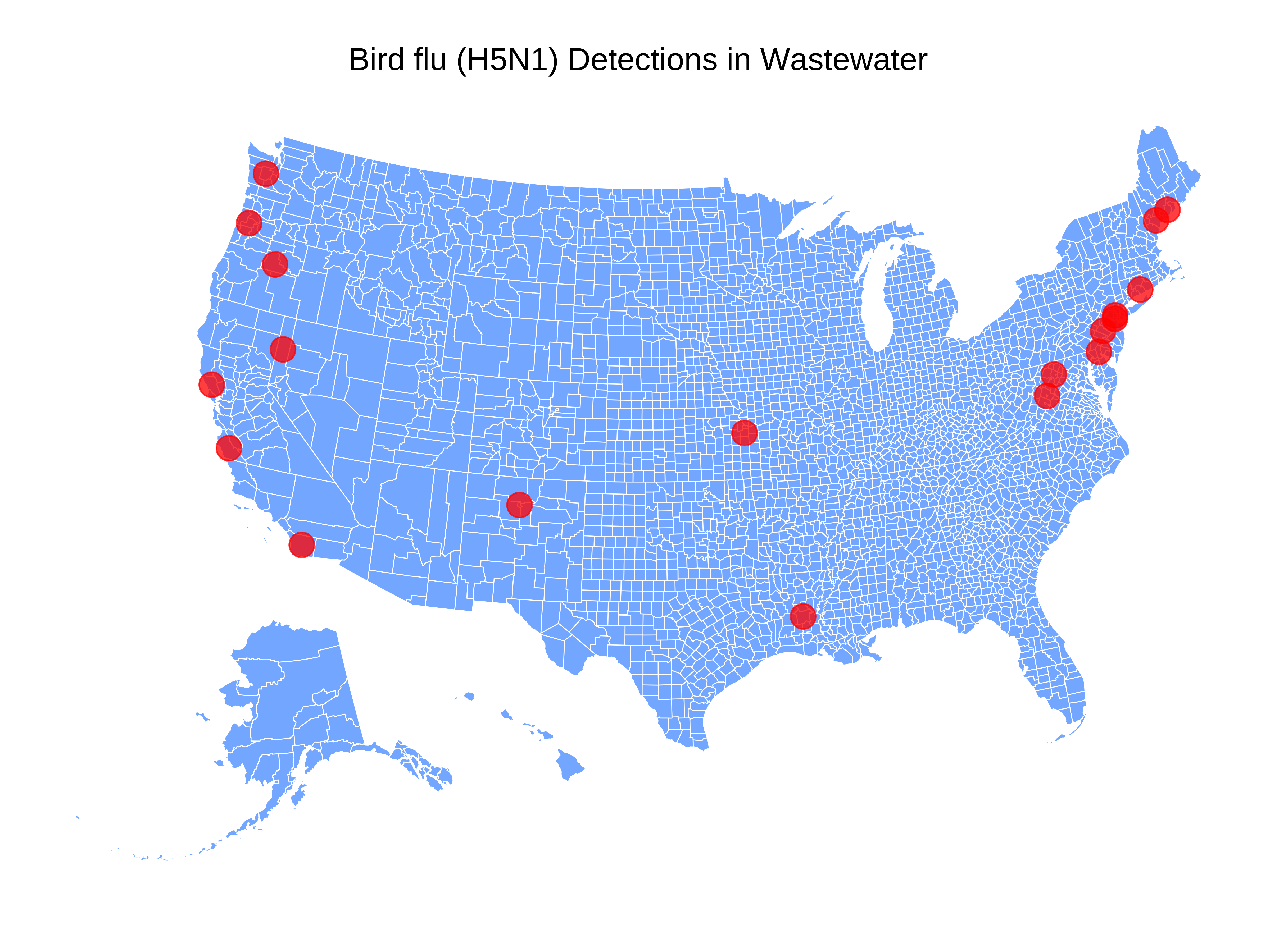
We continue to monitor the evolving H5N1 influenza virus situation. As we do, a quick reminder that Biobot’s influenza A assay detects the H5N1 influenza subtype, which is an influenza A virus, but does not distinguish between the different subtypes of influenza A (e.g. H5N1 vs H1N1). Thankfully, we still have not seen large, widespread increases in influenza A concentrations. We will share any important updates via Twitter and in the risk reports.
Wastewater data from Biobot Analytics for RSV, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2 are through October 5, 2024 (MMWR week 40). Clinical data for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19 are from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updates to clinical data are through September 28, 2024 (MMWR week 39).