At Biobot, we analyze wastewater across the country for various infectious disease pathogens....

Respiratory Virus Risk Reports
Comprehensive Insights for COVID-19, Influenza, and RSV
Influenza and RSV Wastewater Monitoring in the U.S. | Week of December 4, 2023
This respiratory season, we are analyzing wastewater for the presence of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza virus (types A and B). Together with COVID-19, these three pathogens are outsized contributors to our seasonal respiratory illness burden. In this data series, we’ll guide you through the wealth of data we’ve gathered from our Biobot Network of national sampling sites, aiming to shed light on emerging trends in respiratory virus activity and community viral load. Our goal is to equip you with information to make informed decisions, especially as we approach the holiday season and gather with family and friends.
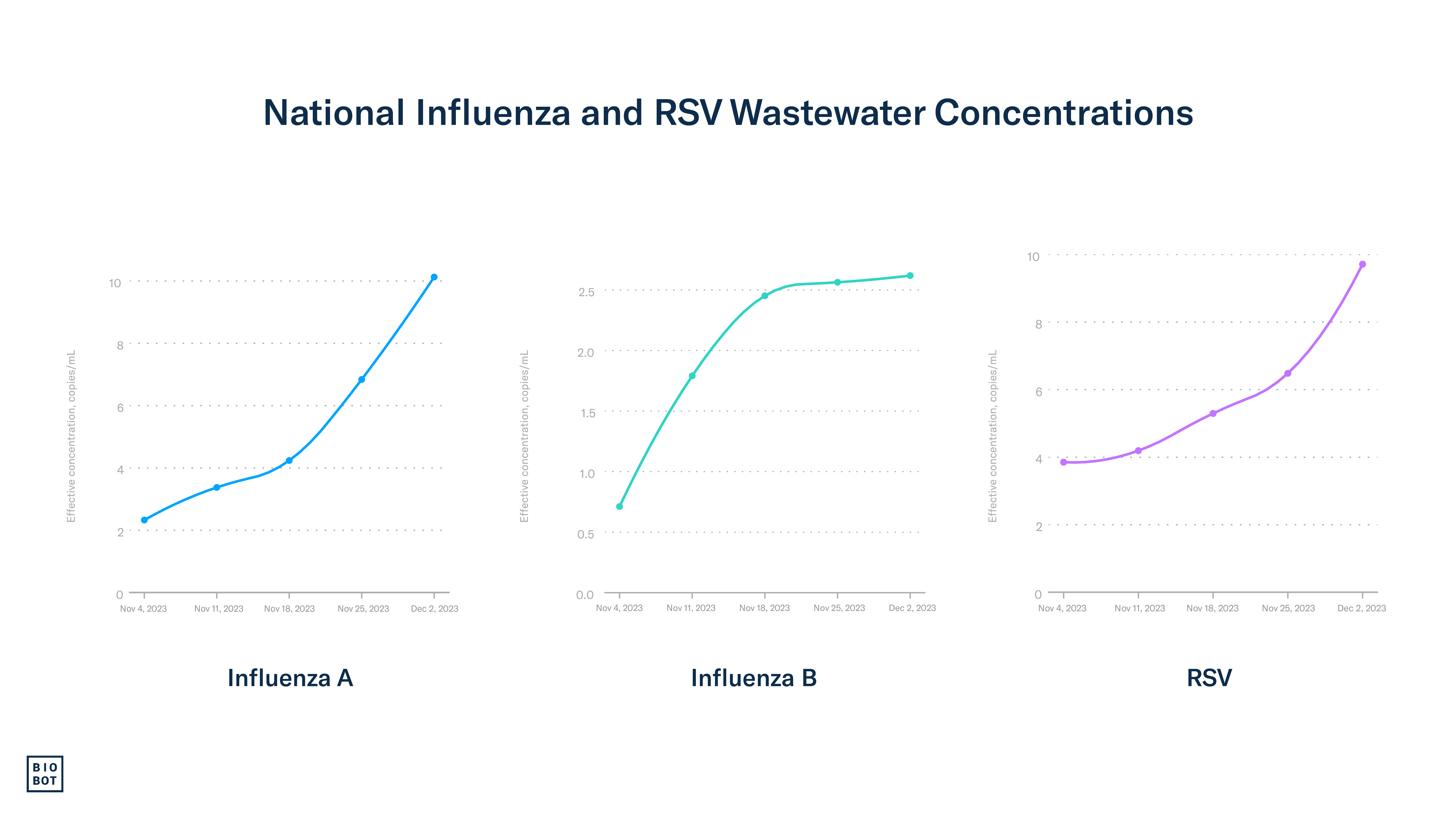
Data Note: Samples are collected from participating locations and processed by our lab team on a rolling basis. Each point on the figure represents the weekly average concentration from Sunday – Saturday (corresponding to the MMWR week), aligned to that week’s Saturday.
Contributors

Marisa Donnelly, PhD
Public Health Partnerships Epidemiologist

Max Imakaev, PhD
Data Scientist
Previous Risk Reports
A note about this week’s report: Biobot’swastewater data for influenza, RSV, and SARS-CoV-2 extends through December 2nd (MMWR Week 48). The most recent clinical data for influenza and RSV available on CDC dashboards are through November 25, 2023 (MMWR Week 47), which we reported on last week. Notably, there haven’t been any changes in the clinical data for flu and RSV compared to the previous week’s findings. The CDC has updated its clinical COVID-19 dashboard to encompass data through November 25, 2023 (MMWR Week 47), and we have integrated this updated information into this week’s report.
Summary: Week of 12/04/23
The respiratory illness season is now in full swing across the US. Biobot’s wastewater data shows active and increased co-circulation of RSV, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2. Clinical data shows that RSV transmission continues to be high. Influenza transmission is on the rise throughout all regions of the US, primarily driven by influenza A. While influenza B is also circulating, its prevalence is notably lower compared to influenza A. Wastewater and hospitalization data show that COVID-19 is also on the rise again, especially in the Midwest and Northeast and we expect there to likely be more hospitalizations and emergency department visits occurring over the next couple of weeks.
The Bottom Line: Respiratory illness season is in full swing and has not yet peaked. With the holiday season also underway – where we travel to gather and celebrate with loved ones – it is a good time to think about taking steps, like staying home if you are sick or getting vaccinated, to keep yourself and loved ones healthy.
RSV
RSV transmission is currently high and continues to increase.
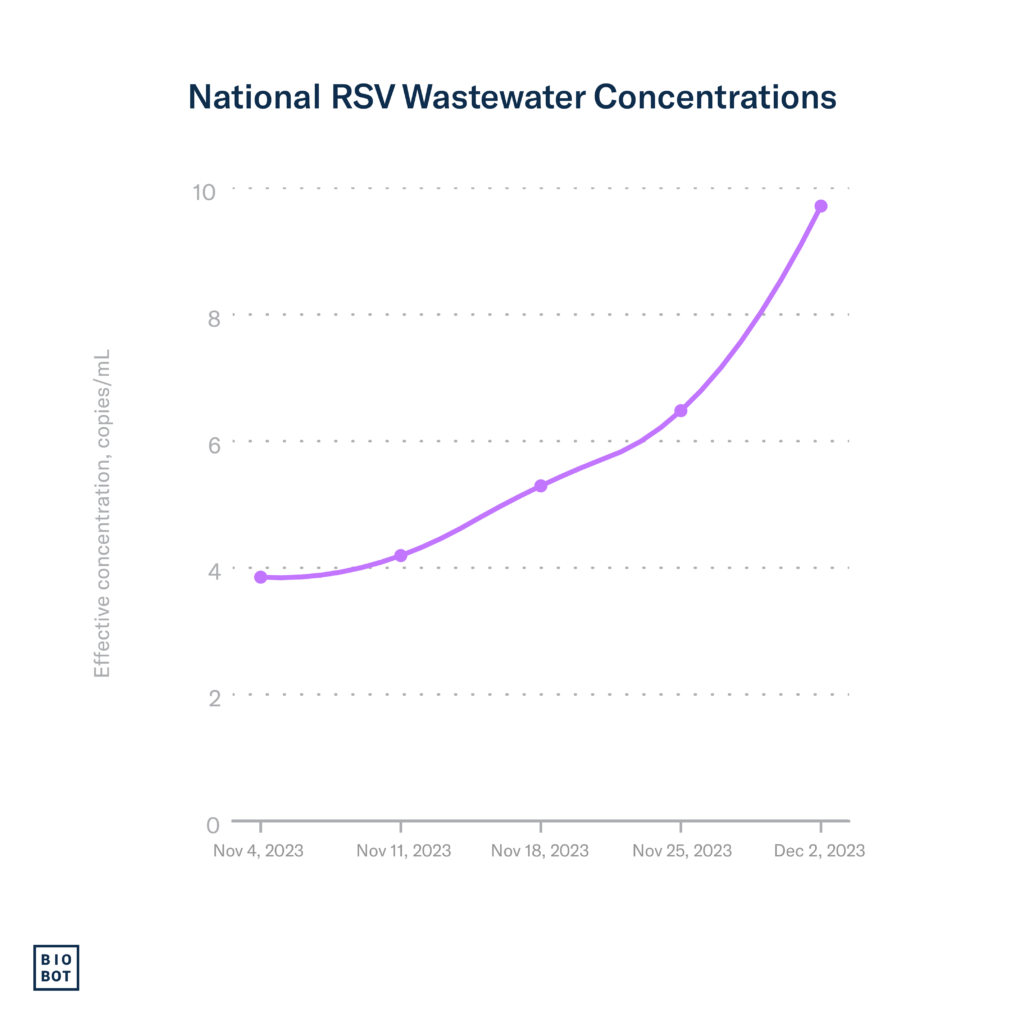
Wastewater data: Using Biobot’s national network of sample providers, we began testing for RSV in wastewater across the country in October, and,since then, the concentration of RSV has been steadily increasing. Data through December 2nd (MMWR week 48) show wastewater concentrations for RSV continuing to increase, with the highest concentrations occurring in the Northeast. The Midwest and South are also showing strong increases in RSV wastewater concentrations, while concentrations in the West remain stable compared to last week.
Clinical data: Data through November 25th (MMWR week 47) show that RSV prevalence is on the rise, both in terms of the number and percentage of positive tests for RSV, with the current national positive PCR detection percentage at about 13%. While hospitalization rates for young children under 4 years old and for individuals aged 65 years and older may be showing signs of slowing, they remain high. The percentage of hospital visits for flu-like symptoms – common among flu, RSV, and COVID-19 patients – is currently at 3.9%.
Southern parts of the US continue to be hit the hardest with RSV, evident in clinical and wastewater data. The percentage of positive PCR tests for RSV in the south is 21%, markedly higher than the national average of 13%. The Northeast region is also experiencing increased levels of RSV activity, with about 14% of PCR tests positive. All other regions also experienced increases in the percentage of PCR tests positive for RSV compared to the previous week.
Contrary to trends around this time last year, when RSV hospitalizations had already peaked, current clinical and wastewater data suggest sustained increases in RSV activity. The percentage of positive tests, hospitalizations, and wastewater concentrations are all still high, suggesting that the peak of the RSV season may still be ahead of us.
Influenza
This week’s wastewater and clinical data continue to indicate that influenza activity is picking up.
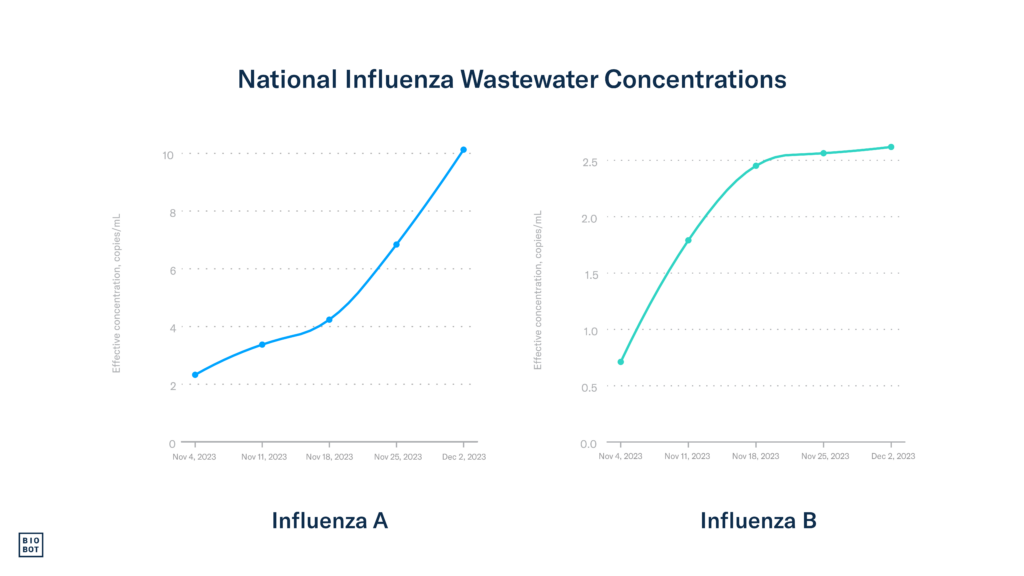
Wastewater data: Using Biobot’s national network of sample providers, we began testing for influenza types A and B in wastewater across the country in October, and since then, wastewater concentrations have continued to steadily increase. Data through December 2nd show influenza A wastewater concentrations increasing while influenza B concentrations remain stable. Wastewater concentrations for influenza A are currently increasing most rapidly in the Northeast and Midwest regions, with the South and West also showing strong upticks.
Clinical data: Nationally, clinical data show that influenza transmission is on the rise, with an increasing percentage of positive tests – currently standing at 6.2%. Concurrently, weekly flu-related hospital admissions are on the upswing. The percentage of hospital visits for flu-like symptoms, a commonality among flu, RSV, and COVID-19 patients, has also seen an uptick to 3.9%.
Similar to RSV, the South is feeling the brunt of the effects. They have more hospital visits for flu-like symptoms than other parts of the country, indicating a higher level of flu activity compared to other areas. Recently, the West also started showing higher levels of influenza-like-illness activity.
Most of the positive flu tests continue to be positive for influenza A, which tracks what we’re finding in wastewater samples. This suggests that influenza A is being transmitted more than influenza B at the moment.
COVID-19
COVID-19 activity and community viral load are increasing – currently, there are more hospitalizations and deaths for COVID-19 than for flu or RSV.
Wastewater data: Wastewater concentrations for SARS-CoV-2, our earliest indicator for understanding transmission trends, have been increasing across the country over the past six weeks. As of December 2nd, the national average is 760 copies/mL, which is 28.4% greater than it was last week (592 copies/mL). The national average concentration is currently lower than it was this time last year (~910 copies/mL). Wastewater concentrations are currently highest in the Midwest at 1,261 copies/mL, which is higher than it was this time last year (~959 copies/mL).
Clinical data: As of November 25th, the most recent week with available COVID-19 clinical data from CDC, the percentage of COVID-19 tests that are positive has increased to 10% nationwide, compared to 8.2% in our last report. Percent positivity remains highest and is currently increasing in HHS region 7 (the Midwest), at about 16.2%, up from 14.1%. Hospitalization rates for COVID-19 have increased by about 10% in the week ending November 25th, resulting in 19,444 hospitalizations.
The most recent CDC data shows that the percentage of positive tests and the number of people visiting the hospital or emergency department for COVID-19 have started increasing in most regions of the country. With additional evidence of increases in SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations, we expect to see test positivity, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations continue to increase over the next couple of weeks.
Footnotes:
Wastewater data for RSV, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2 are from Biobot Analytics and are through December 2, 2023 (MMWR week 48). Clinical data on testing, hospitalizations, and emergency department visits for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19 are from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updates to clinical data for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19 are through November 25, 2023 (MMWR week 47).