FAQ

How it works
Founded at MIT, Biobot Analytics is a wastewater epidemiology company that analyzes sewage to provide public health analytics. We have worked in hundreds of communities across every US state and have partnered with the CDC, the World Bank, and others.
Wastewater-based epidemiology is the science of analyzing sewage to better understand the public health impact of certain pathogens and chemical compounds within a population. Wastewater contains valuable information on human health because viruses, bacteria, and chemical metabolites are excreted in urine and stool.
Wastewater analysis can detect a broad range of biological and chemical markers, including SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, the influenza virus, high-risk substances (such as opioids), and more.
Wastewater data is:
- Equitable: WBE can serve anyone who uses a bathroom. It does not rely on an individual’s access to or use of healthcare, providing a holistic and inclusive view of epidemiological disease trends.
- Anonymized: Wastewater data represents an aggregate sample of human waste. It is inherently anonymous and cannot be traced back to individuals.
- Cost-Effective: One sample is representative of many individuals in a building or community (e.g. a town or city).
- Flexible: WBE systems can pivot to track the emergence and spread of newly identified infectious diseases, or diseases that are beginning to spread in areas where they were not previously circulating.
- Timely: Because wastewater testing doesn’t need to wait for individuals to become symptomatic, seek medical care, and get tested, WBE can provide very timely data.
- For COVID-19: Wastewater data is both an independent indicator of virus activity, and may reflect trends sooner than case data because of the multiple steps involved before an infected individual is counted as a case. Many states have reduced their case updates to once a week, further delaying case information.
- Comprehensive: WBE is particularly well-suited to detect diseases with a mitigate outbreaks caused by diseases with nonspecific symptoms and/or a pre-symptomatic shedding period (e.g. COVID-19), or diseases spread primarily by asymptomatic carriers (e.g. Hepatitis C).
- For COVID-19: All active infections are captured by wastewater analysis, regardless of one’s vaccination status or the presence of symptoms.
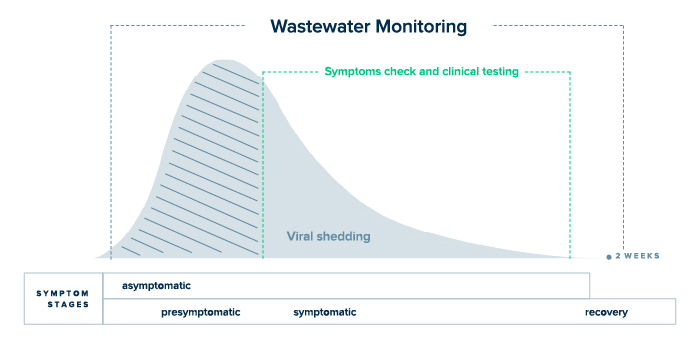
- At this stage in the pandemic, fewer COVID-19 cases are reported because take-home antigen tests are widely available and vaccination has boosted the population’s immunity.
- As a result, clinical testing data has become less dependable, and public health officials are forced to rely on lagging indicators of viral spread, such as hospitalizations and deaths.
- This is why wastewater monitoring will play an even more important role in containing the spread of the virus as life returns to normal.
Sampling
- Samplers (typically located at a wastewater treatment plant or manhole) collect 24-hour composite samples of preferably raw influent (untreated wastewater).
- Samples are packaged in our pre-made kits, then sent via Fed-Ex overnight shipping to our lab in Cambridge, MA (using pre-paid shipping labels).
- Our lab analyzes the samples and sends reports 1-3 business days later.
- Our COVID-19 report provides an overview of samples’ SARS-CoV-2 concentrations, their trends over time, and how they compare to other samples in our database.
Data
- Very well. Throughout the pandemic, our dataset—drawn from large and small communities across the country—accurately reflected both localized peaks and nationwide surges.
- When the availability of reliable clinical reporting fluctuated during the Omicron wave, our data showed much higher levels of COVID-19 than reported cases. As asymptomatic cases, at-home tests, testing fatigue, and other factors impact clinical reporting in subsequent waves, wastewater data will continue to be a strong, independent (yet complementary) indicator of the total number of infections.
We have not seen evidence of any substantial change in SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding due to any of the variants, including Delta and Omicron. In fact, wastewater data provided an estimate of clinical case under-reporting during the Omicron wave.
No. The vaccine is not a live virus, does not cause an infection, and is not shed in stool. Vaccination and boosting reduces the total number of infections in a community, but we have not seen evidence that vaccination substantially changed the per capita fecal shedding of the virus. Read our blog post here for more.
No. From the point of view of wastewater, they are the same as a normal infection.